Viral reproduction process:
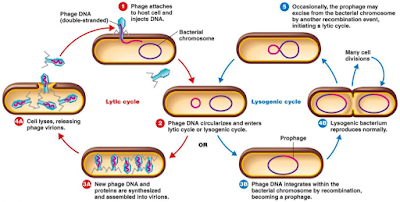
Viruses can reproduce within the host cell in two processes of a cycle. The multiplication of virulent phages is called lytic cycle and the multiplication of template phages is called lysogenic cycle.
Lytic cycle:
It is considered the main cycle of viral reproduction as most of the viruses replicate in this process. At this cycle, viruses are entered their genetic material within the host cell. Then it transcribes itself into the host cell's messenger RNAs and uses them to direct the ribosome. The host cell's DNA is destroyed and the virus takes over the cell's metabolic activities. The virus starts using the cell energy because of its own propagation. The virus produces progeny phages. These replicate fast, and soon the cell is filled with approximately 100-200 new viruses. As the cell starts getting overcrowded, the initial virus releases enzymes to destroy the cell wall. The cell wall bursts - this method is called lysing - and the new viruses are released.
Lysogenic cycle:
In this cycle, the viral genetic material enters the host cell and integrates into the host DNA as a new set of genes called prophage. So, the viral DNA becomes part of the cell's genetic material. No progeny particles, like in the lytic phase, are produced. Each and every time the host cell DNA chromosome replicates during cell division, the passive and non-virulent prophage replicates too. This can modify the cell's characteristics, but it does not destroy it.






0 comments:
Post a Comment